The Full GEO Stack: 5 Core Disciplines and the Toolkit to Dominate AI Search in 2025

You're looking at your reports and you don't understand what's happening. Top-3 rankings, normal CTR, but organic traffic is either stagnant or slowly declining. More and more specialists are feeling this 'invisible wall' effect - traffic simply isn't reaching the site.
The reason - generative AI answers. Google's AI Overviews creates a ready-made answer directly on the search page, compiling information from your site and your competitors' sites. The user gets the facts, product comparisons, or instructions they need and leaves without ever clicking a blue link. Your content did all the work, but the result is zero clicks. This means that SEO in its classic form, the fight for the top 10, no longer guarantees results.
Welcome to the era of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). Here, the primary goal isn't to hold a position, but to become the primary source. To ensure AI algorithms cite your data, recommend your brand, and reference your site as the ultimate authoritative source. And to win this new game, a single all-in-one tool isn't enough. You need a systematic approach and a full arsenal - a working stack where each service solves its specific task.
In this article, we will break down GEO into its 5 core components - from analytics and content creation to PR and reputation management. We will assemble a ready-to-use toolkit for you, which will help you transform chaotic attempts to 'please the AI' into a systematic and measurable process.
Block 1: Analytics & Measurement - Your Command Center
You can't manage what you can't measure: laying the foundation for your strategy
All work in Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) begins and ends with analytics. Without precise data, you are operating blind. All your efforts in content creation, technical optimization, and PR are meaningless if you cannot measure their impact on your visibility in AI-generated answers. This is the starting point that reveals your weaknesses and the final report that proves your strategy's effectiveness. A professional GEO analytics stack consists of three layers, each one critically important.
Tool #1: Geometrika (The AI & LLM Citation Analytics Center)
Geometrika dashboard overview
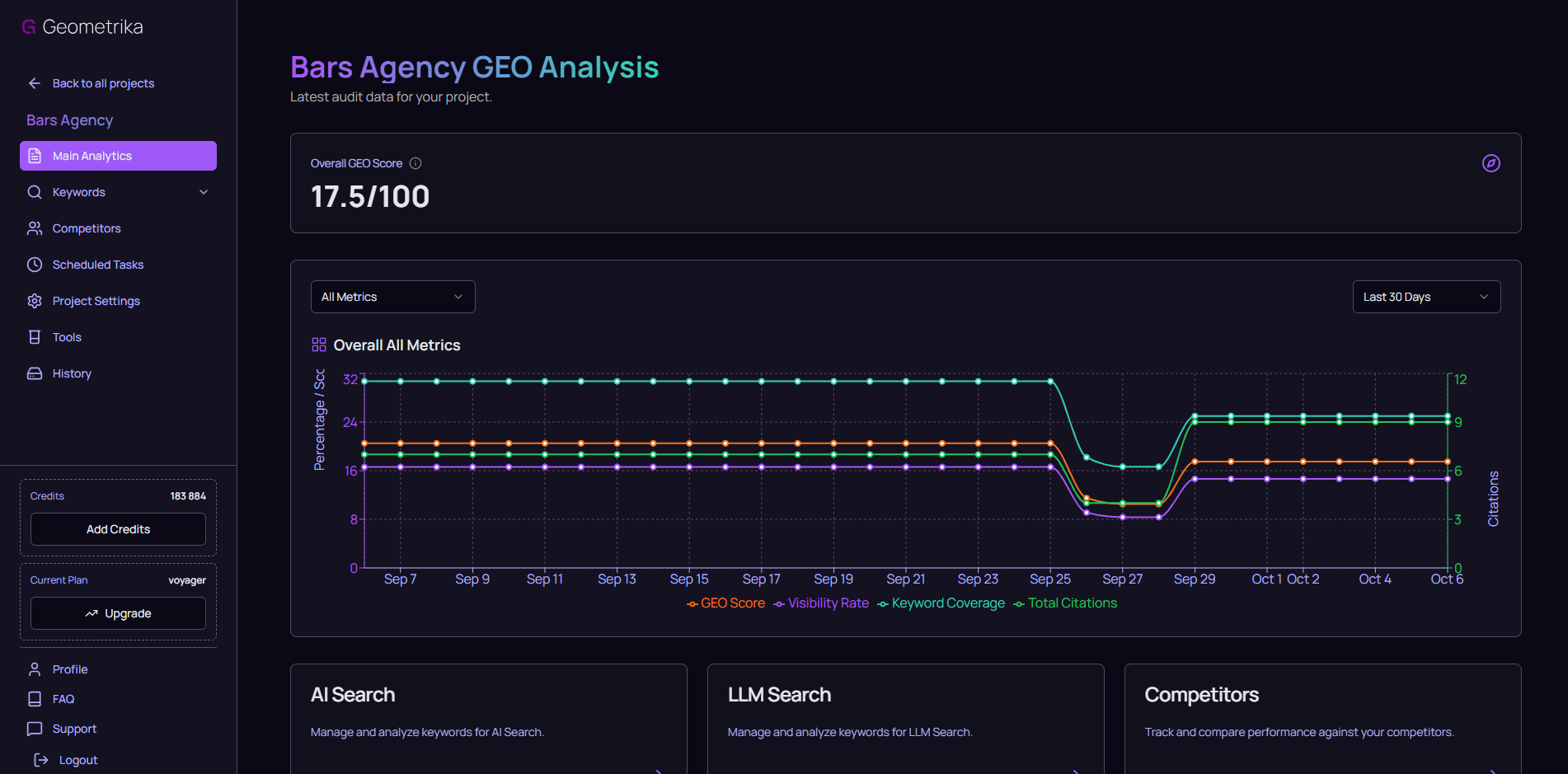
This is your primary navigation instrument in the world of GEO. It provides an entirely new layer of data that neither web analytics platforms nor classic SEO suites can offer.
- GEO Score - Your Master KPI
To manage the process, you need a single, understandable metric. The GEO Score is an integral rating from 0 to 100 that shows your website's authority in the eyes of neural networks. This is not an abstract number - it's a metric that accounts for two key factors: citation frequency (how often AI systems reference you) and query coverage (what share of your target semantic core you cover). This transforms the abstract task of "pleasing the AI" into a concrete, measurable goal: "increase GEO Score from 30 to 50 in one quarter." - AI Search vs. LLM Search Analysis - Two Different Battlegrounds
Geometrika intentionally separates analytics into two key environments because the mechanics and objectives differ:- AI Search (Google AI Overviews + Yandex AI mode): This is a battle for citations on specific informational and commercial queries from your semantic core. The goal is to become the primary, most complete, and factually accurate source for the search engine.
- LLM Search (ChatGPT, Grok, Gemini, Claude, Perplexity): Here, users seek advice, comparisons, and recommendations more than just facts. Being featured in these answers directly impacts brand reputation and awareness. It's a more complex game tied to your overall authority online.
- Competitive Analysis - Who is AI really learning from?
The service shows which other sites the neural network cites for your queries. These are your actual GEO competitors, and they often do not overlap with those you fight in the top 10 organic results. Geometrika uncovers non-obvious rivals- for instance, a niche blog or a forum that the AI has deemed a more authoritative source on a specific topic than your commercial website.
Tool #2: SEO Platforms (The Classic SEO Center)
Ahrefs
- Example: Semrush or Ahrefs.
- Role: Monitoring positions in the traditional organic search results, conducting keyword research, and performing baseline competitive analysis. This tool shows your fundamental search engine visibility - the "blue links." In the GEO era, its role has not diminished but transformed: it is now your "health indicator" and a data provider for deeper analysis.
- Key Functions for the GEO Stack:
- Rank Tracking: It's still necessary to track positions in the top 30/50. A site that is invisible to a search engine has zero chance of being sourced for a generative answer.
- Keyword Research: These platforms are used to build and expand the semantic core that you will then upload to Geometrika for citation analysis.
- SERP Analysis: Understanding the landscape of the traditional search results page is crucial context for your GEO strategy.
Tool #3: Web & Product Analytics (The User Behavior Center)
Hotjar
- Example: Google Analytics 4, supplemented with Hotjar or Microsoft Clarity.
- Role: Analyzing the traffic that actually reaches your site and how users behave on it. GA4 answers "what" happened, while tools like Hotjar answer "why."
- Key Functions for the GEO Stack:
- Traffic & Conversion Tracking (GA4): Provides the hard numbers on traffic sources, user flows, and goal completions. It confirms whether your GEO efforts translate into business results.
- Behavioral Analysis (Hotjar/Clarity): Session recordings and heatmaps are indispensable for usability analysis. If Geometrika shows that an AI stopped citing you in favor of a competitor, watching session recordings may reveal why. Perhaps the competitor's article has a better structure, a calculator, or a video that holds user attention better- a strong signal for AI algorithms.
How it all works together: from hypothesis to conclusion
Imagine you see a traffic drop for a key query cluster like "best running shoes for flat feet."
- Check Semrush. Your organic ranking is stable at #3. The problem isn't classic SEO.
- Open Geometrika. You analyze the same query and see that the Google AI Overview is now citing a niche running blog from page 2 of the organic results in 80% of cases. Your GEO Score for this cluster has plummeted from 45 to 10. You have found the reason for the traffic leak.
- Go to Google Analytics & Hotjar. GA4 confirms the overall drop in organic entrances to that page. Then, in Hotjar, you watch recordings of the few users who do arrive. You see them scroll briefly and leave. An analysis of the competitor's page reveals an interactive shoe-finder quiz and video reviews.
The data from all three systems provides a complete, actionable picture. Semrush says your basic SEO is fine. Geometrika pinpoints the exact cause- a loss of citation in AI Overviews to a specific competitor. GA4 and Hotjar help form a hypothesis as to why it happened- your content is less engaging and useful. You know exactly what to do: not to push your rank from #3 to #2, but to radically improve your page's content and user experience.
Block 2: Content Creation & Optimization - Fuel for AI
How to create content that neural networks will want to cite
AI algorithms are not human. They don't appreciate beautiful metaphors, but they are obsessed with facts. They won't be impressed by an author's unique prose, but they are thrilled by clear structure. For your content to become a primary source for them, it must be impeccable from three perspectives: factual accuracy, logical structure, and measurable utility for the end-user. The process of creating such content can be broken down into three mandatory stages.
Stage 1: Building the Foundation - AI for Generating Structure and Drafts
ChatGPT
Starting from scratch is slow and expensive. Modern language models are the perfect tool for a quick start, if used correctly. They act not as the author, but as a hyper-efficient assistant who handles all the rough work.
- Tools: ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini.
- Role: Idea generator and rough draft writer.
- Key Tasks for GEO:
- Generate a comprehensive structure: This is their most valuable function. Instead of guessing what questions your audience has, you can directly delegate this to an AI.
- Example Prompt: You are an SEO specialist and an expert photographer. Create a maximally detailed, nested structure for an article on the topic "How to choose a mirrorless camera for beginners." Include all key parameters: sensor size (Full-Frame, APS-C), resolution, autofocus systems, video capabilities (4K, 1080p), and top brands. Include a comparison section against DSLRs and a comprehensive FAQ block.
The response will be a ready-made skeleton for your article with H2-H4 headings that already covers most aspects of the topic. This ensures topical completeness - a key factor for AI.
- Example Prompt: You are an SEO specialist and an expert photographer. Create a maximally detailed, nested structure for an article on the topic "How to choose a mirrorless camera for beginners." Include all key parameters: sensor size (Full-Frame, APS-C), resolution, autofocus systems, video capabilities (4K, 1080p), and top brands. Include a comparison section against DSLRs and a comprehensive FAQ block.
- Write the first draft: After approving the structure, you can have the AI write a draft for each section. This saves dozens of hours of a copywriter's time. The text will be raw, but it will exist. You go from a blank page to the editing stage in minutes.
- Expand on ideas: AI excels at the task of "thinking outside the box."
- Example Prompt: I'm writing an article on choosing a mirrorless camera. What other related but important topics have I missed? Should I add information about lens mounts, battery life, or essential accessories?
This helps to make your content not just good, but the best and most complete in your niche.
- Example Prompt: I'm writing an article on choosing a mirrorless camera. What other related but important topics have I missed? Should I add information about lens mounts, battery life, or essential accessories?
- Generate a comprehensive structure: This is their most valuable function. Instead of guessing what questions your audience has, you can directly delegate this to an AI.
Critically Important Note: AI is an intern, not your editor-in-chief
Never, under any circumstances, publish AI-generated text without thorough manual review and revision. The quality of the output is 100% dependent on three factors:
- Prompt Quality: The "garbage in, garbage out" formula works perfectly here. The more detailed, specific, and contextual your request, the better the result.
- Model's Data Freshness: AI models can "hallucinate" - invent facts, brands, and specifications. All factual information (numbers, dates, names, parameters) must be double-checked against reliable sources.
- Brand Voice and Tone: Raw AI-generated text lacks personality. It's bland and generic. Your task in the next stages is to infuse it with expertise, real-world examples, and your brand's unique voice.
Stage 2: Shaping and Styling - AI Humanizers
Undetectable.Ai
Once you have a factually accurate draft, it needs to be processed. "Humanizing" the text is not an attempt to deceive AI, but a way to make the content better for both people and the algorithms themselves.
- Tools: Undetectable.ai, QuillBot, and other next-generation paraphrasing tools.
- Role: Stylistic editor.
- Why this is necessary for GEO:
- Increase User Trust: Texts written in a sterile, robotic tone have high bounce rates. People sense inauthenticity, don't finish reading, and leave. A high bounce rate is a powerful negative signal for search engines and AI, which says: "this content does not solve the user's problem."
- Reduce Detection Risk: Advanced AI algorithms are trained on vast text corpora and can "see" the typical patterns, phrases, and structures characteristic of machine generation. A text with a unique, more complex syntax and vocabulary has a better chance of being perceived as original authorial material, and therefore, as a primary source.
- Create a Natural Style: Humanizer services paraphrase sentences, change their structure, and find synonyms, ridding the text of repetition and typical AI phrases like "it's important to note" or "in conclusion."
Stage 3: Final Polish and Quality Control - Text Editing Services
Grammarly

This is the last line of defense before publication. Here, you eliminate anything that might prevent an AI from considering your text as a benchmark.
- Tools: Grammarly (Premium), Hemingway App, Copyscape.
- Role: Quality Control Department.
- How each tool works for GEO:
- Hemingway App: Its job is to fight for information density and clarity. The service ruthlessly cuts out "fluff" by highlighting long, complex sentences, passive voice, and excessive adverbs.
- Connection to GEO: To form an answer, AI algorithms need to extract facts and entities from your text. The less verbal garbage there is, the easier it is for the AI to "drink" the essence. A text with a high readability score in Hemingway is typically packed with useful information, which is a direct signal of its value.
- Grammarly (Premium): This service assesses not just grammar, but also clarity, engagement, and tone.
- Connection to GEO: A text overloaded with keywords is perceived by modern algorithms as a manipulation attempt, not as useful content. Such materials will be ignored or penalized by AI. Grammarly helps find the balance between SEO necessity and natural language, improving readability and user engagement signals.
- Copyscape: Its primary function is to check for uniqueness and plagiarism.
- Connection to GEO: This is the most obvious and crucial point. The goal of AI is to find the primary source. A text with low uniqueness is, by definition, not a primary source. It is derivative. The chance of such content being cited approaches zero. In today's environment, the uniqueness requirement for core content is 95-100%.
- Hemingway App: Its job is to fight for information density and clarity. The service ruthlessly cuts out "fluff" by highlighting long, complex sentences, passive voice, and excessive adverbs.
From Draft to Asset - The Content Production Line
The three-stage process described is not a set of recommendations, but a production line.
- AI Models supply the "raw material" - a structured but soulless and factually raw text mass.
- An Expert and an Editor turn the raw material into a "semi-finished product" - they verify and add facts, examples, and expertise.
- A Humanizer gives the product its "marketable appearance" - a natural style and readability.
- QC Services act as the "quality control department," rejecting defects before the content is sent for publication.
Skipping any stage devalues the entire effort. An unverified AI draft is a risk to your reputation. A humanized but fluffy text has no informational value. A unique but keyword-stuffed piece will be ignored. Only by consistently following all these stages can you create not just an "article," but an information asset - a unit of content designed with the sole purpose of becoming an exhaustive, reliable, and easily citable primary source that an AI will choose over hundreds of others.
Block 3: Technical Optimization - The Foundation of Accessibility

Give AI Crawlers the Green Light
The most brilliant, useful, and factually accurate content is absolutely worthless if AI bots cannot find it, crawl it, and, most importantly, correctly understand its structure and meaning. Technical optimization for GEO is not a secondary task- it is a fundamental requirement. It is the logistics that deliver your "fuel" to the engine of artificial intelligence.
Tool #1: Crawlers & Search Console (The Technical Audit)
Screaming Frog SEO Spider
These tools allow you to look at your site through the eyes of a robot and find all obstacles in its path. Their job is to ensure unimpeded access to all important content.
- Examples: Google Search Console, Screaming Frog SEO Spider.
- Role: Conducting a full technical audit of the site. These tools are not interchangeable- they complement each other.
- Google Search Console is your car's dashboard. It shows you how the search engine already sees your site, what problems it has found, and provides official recommendations.
- Screaming Frog is the full diagnostic check at the auto shop. It allows you to proactively crawl your site yourself, find problems before they become critical, and look into the deepest corners of your resource.
- Key Checkpoints for GEO:
- Checking robots.txt - The Main Gateway.
The robots.txt file is the first place any bot looks. An error in a single line can block your entire site or its key sections from being indexed. In the context of GEO, a standard check is no longer sufficient.- What to check: Ensure you do not have Disallow: directives for specialized AI crawlers. Primarily, these are:
- GPTBot (OpenAI's crawler for ChatGPT)
- Google-Extended (the crawler that gathers data for Google's models, including Gemini)
- ClaudeBot (Anthropic's crawler)
Many sites, out of old habit or paranoia, may have blocked all "non-standard" bots, which today is equivalent to shooting yourself in the foot. Your robots.txt should be as open as possible to known and trusted AI agents.
- What to check: Ensure you do not have Disallow: directives for specialized AI crawlers. Primarily, these are:
- Finding Broken Links (404 Errors) and Improper Redirects.
Every broken link is a dead end for a crawler. It reaches it and stops, wasting precious crawling budget. Redirect chains (e.g., from HTTP to HTTPS, from www to non-www, and then to a new page version) slow down crawling and can result in the bot never reaching the final URL.- How this affects GEO: AI systems value reliability and source integrity. A site riddled with broken links looks abandoned and outdated. This undermines its authority. Screaming Frog is ideal for finding all 404 errors and redirect chains on your site.
- Analyzing Page Speed.
Speed is not just a ranking factor- it is an accessibility factor. AI models operate on huge volumes of data and need to retrieve it quickly. A slow, unresponsive site is an unreliable information provider.- What to check: Use reports in Google Search Console and tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to analyze Core Web Vitals (LCP, INP, CLS). Ensure your server delivers content quickly and that pages are not overloaded with heavy scripts and images. For an AI, a slow site equals an unavailable site.
- Checking robots.txt - The Main Gateway.
Tool #2: Schema Validators (The Translator for AI)
Schema.Org
If the technical audit ensures access to the content, schema markup ensures its understanding. This is the most direct way to communicate with AI.
- Examples: Google's Rich Results Test, the Schema.org Validator.
- Role: Implementing and verifying Schema.org structured data. This is your "translator" from human language to machine language.
- How it works with a simple example:
Imagine you have an article "How to Choose a Bicycle." In HTML code, it looks like a set of headings and paragraphs. A human understands its structure intuitively. But for a robot, it's just text.
With Schema.org markup, you turn this text into a structured object. You aren't just writing an article- you are telling the robot:- "This block ("HowTo") is an instructional guide."
- "This item ("HowToStep") is a specific step in this guide, for example, 'Determine your riding style.'"
- "And this block ("FAQPage") contains answers to frequently asked questions."
- "The Question is 'What is the best bicycle for the city?', and the Answer is 'For the city, a hybrid bicycle is the best choice...'"
- This increases the chances of citation exponentially. When a user asks "what bike to choose for the city," the AI is far more likely to take your clearly marked answer than to try and "extract" it from a competitor's block of plain text.
- Key Schema Types for GEO:
- Article: Basic markup for any article, indicating the author, publication date, and publisher. A signal of freshness and authorship.
- FAQPage: Critically important for being featured in answer blocks. Each question and answer must be clearly marked up.
- HowTo: Ideal for instructions, recipes, and step-by-step guides.
- Product: For e-commerce sites. Allows you to convey price, availability, ratings, and reviews.
- Organization: Markup for your company information (name, address, phone number). Increases trust.
An Open Door and a Common Language - The Bare Minimum
Technical optimization in the context of GEO is not about micro-improvements- it's about eliminating fundamental barriers. Crawlers and search consoles ensure that the door to your site is always open and free of obstacles. Schema validators ensure that upon entering that door, the robot can not just "see" the text, but read and understand it as if it were holding a detailed instruction manual. Without this essential foundation, your excellent content risks going unnoticed by its most important reader - the artificial intelligence.
Block 4: PR & Authority Building - External Signals

Why what others say about you is more important than what you say about yourself
AI algorithms form their "opinion" of your brand not based on the marketing claims on your website, but by analyzing the entire public internet. They are searching for objective signals of trust. A mention of your brand, product, or expert on an independent, authoritative resource is not just a link. It is a third-party verification of your expertise. It is a digital validation of your status.
For an AI model striving to provide the most reliable answer, a brand that is regularly cited in quality media is an order of magnitude more authoritative than a silent competitor. Building this "information echo" around your company is a deliberate effort, conducted on two key fronts: reactive and proactive.
Tool #1: HARO (Help A Reporter Out) & Qwoted (The Reactive Strategy - Expertise on Demand)
HARO
These services turn passive waiting into an active opportunity. They act as a bridge between journalists looking for sources and expert opinions for their articles, and the companies ready to provide that expertise.
- Role in the Stack: Becoming a source for authoritative media outlets by responding to their queries.
- How it Works:
- The Query: A journalist from a publication like Forbes, The Wall Street Journal, or a niche industry journal posts a query: "Seeking a financial analyst to comment on the latest Fed rate hike."
- The Response: As an expert in your field, you provide a concise, insightful, non-promotional comment backed by facts.
- The Result: The journalist includes your comment in their article, citing your name, title, and company. Often, this comes with a backlink.
- Value for GEO: Building the AI's Knowledge Graph
This is far more than just link building. When an AI crawler scans a new article on a major media site, it performs Named Entity Recognition (NER). The phrase "According to Jane Doe, Head of Analytics at 'SuperAnalytics Inc.'..." breaks down into three key, interconnected objects for the AI:- The Expert (ENTITY: PERSON): "Jane Doe"
- The Brand (ENTITY: ORGANIZATION): "SuperAnalytics Inc."
- The Topic (CONTEXT): e.g., "financial markets" (inferred from the article's title and content).
- The AI then builds connections in its internal knowledge graph. Here's what it's actually "learning":
- Experience & Expertise (the first two E's in E-E-A-T): The AI establishes a strong link: the entity "Jane Doe" is associated with the topic "financial markets." This is not abstract knowledge, but the validated experience of a specific person.
- Authoritativeness (A): The AI builds a second link: the entity "Jane Doe" is affiliated with the entity "SuperAnalytics Inc." The expert's personal authority becomes associated with the brand.
- Trustworthiness (T): This entire structure (Expert -> Brand -> Topic) is validated by a third party - an authoritative media outlet acting as a "notary."
- With each new publication, these connections in the AI's knowledge graph grow stronger and more reliable. You are purposefully building the public profile of your key employees as recognized experts. Their personal authority becomes a transferable digital asset for the entire company.
Tool #2: EIN Presswire / Brandpush (The Proactive Strategy - Mass Information Distribution)
EIN Presswire
If HARO is about precise, reactive strikes, then press release distribution services are about planned, proactive campaigns to create a massive information field.
- Role in the Stack: Creating an "information spike" and ensuring broad coverage for significant news.
- How it Works:
- Create the News Hook: You prepare one strong piece of content - a press release. This could be a product launch, new research findings, an event announcement, or a major company milestone.
- Choose Distribution & Send: You select a distribution circuit based on your target audience (e.g., National, Tech, Financial). A service like PR Newswire then wires your release across its vast, segmented network of newsrooms, journalists, and media outlets.
- Guaranteed Pick-up: The release gets picked up and published across a wide array of news sites, industry portals, and syndicated feeds. Your news appears on dozens or even hundreds of domains.
- Value for GEO: Creating Mention Density and Context
The value here is not in getting one link from a top-tier site, but in creating mass and density of mentions.- Forging a "Digital Footprint": In a single push, you get hundreds of mentions of your brand or product. To an AI algorithm, this looks like a significant event that many are discussing. It's a signal of importance and relevance.
- Hitting the News Wires: A key advantage is that top services feed directly into news terminals like the Associated Press, Google News, and Apple News. These are high-trust sources, and information from them carries extra weight for AI models.
- Creating Context at Scale: The mass publication of a release with the same headline and content creates a powerful associative link. The AI quickly learns that your "Product X" is related to solving "Problem Y" because it sees this connection confirmed across 50+ different domains simultaneously.
The Reactive Shield and Proactive Sword of Authority
PR and authority building in the GEO era is a two-part mission. Services like HARO allow you to work on quality, proving your deep expertise and earning mentions on top-tier publications. Press release services like EIN Presswire allow you to work on quantity and reach, proactively building an information field around your key news. Using both tools in tandem creates a powerful cumulative effect. You form a digital echo around your brand that is so dense and positive that AI algorithms have no choice but to recognize you as a primary and trustworthy source in your niche.
Block 5: Reputation Management (SERM) - Conducting the Digital Echo

Control the public opinion that feeds the neural networks
In the old model of SERM (Search Engine Reputation Management), the main goal was to push negative results out of the top 10. In the new reality of GEO, that is not enough. Modern AI models don't just scan search results- they absorb, analyze, and synthesize information from the entire internet. They read reviews on Google Maps, discussion threads on Reddit, comments under YouTube videos, and posts on X and Facebook.
This entire mass of unstructured human speech - from rave reviews to angry rants - becomes the training data for AI. It doesn't just index these mentions- it forms its own "opinion" about your brand based on them. A negative review left unanswered on a popular review site carries more weight for an AI algorithm than five glowing articles on your own website, because it is perceived as objective, unbiased user experience. To manage this process is to directly influence how AI will represent your company to millions of users.
Tool: Brand Monitoring Systems (Your "Ears" on the Internet)
Brand24
To manage your reputation, you must first hear it. In real-time, 24/7. Doing this manually is impossible. That's what automated monitoring systems are for.
- Examples: Brand24, Mention.
- Role: The automatic and continuous collection and analysis of all public mentions of your brand online. This is your early warning system and your channel for market feedback.
- How it Works on a Technical Level:
- Setting up Monitoring Projects: You define the keywords the system should track. This isn't just your brand name ("Acme Corp"), but also product names, key employee names (CEO, brand evangelists), website addresses, and even common misspellings or slang versions of your name.
- Data Collection: Powerful crawlers scan millions of sources: social networks (X, Facebook, Instagram, Reddit, etc.), blogs, forums, news sites, review platforms like Yelp and Trustpilot, and more.
- Analysis and Segmentation: The collected mentions are automatically analyzed. The key here is sentiment analysis. The system determines whether a mention is positive, negative, or neutral. Mentions are tagged and grouped by topic, author, and source.
- Alerts and Reports: You configure alerts. For example, you can receive an instant email or Slack notification for every negative review with a 1 or 2-star rating.
- Practical Application for GEO - From Defense to Offense:
- Defense: Rapidly Neutralize Negativity.
- Scenario: A user posts an angry review on Trustpilot: "Bought your 'Super-Vac 3000,' it broke after one day, and customer service is silent!"
- Without Monitoring: The review sits there for weeks. Hundreds of potential customers read it. The AI model, gathering information about the "Super-Vac 3000," sees this signal. When asked, "what are the problems with the Super-Vac 3000," it will likely include a point about "poor reliability and bad service" in its answer.
- With Monitoring: You receive an alert 15 minutes after publication. Your community manager or support representative responds publicly from the official company account, apologizes, and resolves the user's problem (replaces the vacuum, offers compensation). The user might even update their review to say, "There was an issue, but they resolved it very quickly."
- Result for AI: Now the algorithm sees a completely different story. Not "the brand is bad," but "the brand sometimes has issues, but it resolves them effectively and cares about its customers." This builds an image of a reliable, customer-centric company, which is a powerful positive signal.
- Offense: Amplify Positivity and Gather Insights.
- Scenario 1 (Amplify): A user on a Reddit subreddit writes, "After a lot of research, I bought the 'Super-Vac 3000,' and I'm very happy with it- quiet and powerful."
- Action: Your representative joins the thread, thanks the user by name, and maybe offers a small bonus (a discount on filters). This turns a satisfied customer into a loyal brand advocate and shows everyone in the discussion that you value your audience. The AI registers this positive interaction.
- Scenario 2 (Gather Insights): The monitoring system shows that over the past month, 50 different users on social media have asked the same question: "How do I clean the HEPA filter on the 'Super-Vac 3000'?" This is a direct, unsolicited request from your target audience. You pass this information to your content team, and they create a comprehensive guide with a video titled "The Ultimate Guide to Cleaning and Replacing Your Super-Vac 3000 Filters." This article, which addresses a real user pain point, has an extremely high chance of becoming the primary source for AI on this topic.
- Defense: Rapidly Neutralize Negativity.
From Managing Reputation to Shaping Reality
In the GEO era, SERM is no longer just about cleaning up negative results. It has become the active process of shaping a digital reputation that is fed directly to neural networks. Monitoring systems are your eyes and ears, allowing you to not just react, but to act proactively. A brand that publicly and systematically solves its customers' problems, expresses gratitude for positivity, and uses feedback to create useful content appears immeasurably more reliable and trustworthy in the "eyes" of AI. You are not just managing what is said about you- you are demonstrating your value through action, and AI is learning from those actions.
Bringing It All Together in a Unified Workflow

From Chaos to System: A Cyclical Approach to GEO
We've broken down the five core disciplines and a full arsenal of tools, from analytics platforms to PR services. But tools on their own are just a collection of dumbbells and barbells in the corner of a gym. Without a clear workout plan, without system and discipline, they're useless. Professional Generative Engine Optimization is not a series of chaotic attempts to "write a better article" or "publish a press release somewhere." It is a continuous, manageable, and, most importantly, measurable production cycle.
This cycle consists of four repeatable stages that transform your GEO strategy from a set of disparate actions into a well-oiled machine.
Stage 1: Measurement - Establishing a Baseline Reality
- Tool: Geometrika.
- Action: Before you change anything, you must establish "Point A." You conduct your first, baseline audit of your site. You upload your full semantic core and get objective, cold numbers:
- Your current GEO Score.
- Your citation share in AI Search and LLM Search for each query cluster.
- A list of your actual GEO competitors - the ones the AI prefers to cite instead of you.
- Result: You get a diagnostic map, not guesswork. You no longer think, "it seems like traffic is dropping because of AI." You see concrete figures: "For the commercial query cluster 'buy [product],' our GEO Score is 5, while competitor X has a 75. We are losing."
Stage 2: Planning - From Data to Hypotheses and Tasks
- Tools: Geometrika, Google Analytics 4, Semrush, your own brain.
- Action: Based on the data from the first stage, you form an action plan. Analyzing the diagnostic map allows you to find the most obvious growth points and formulate working hypotheses.
- Hypothesis 1 (Content): "Geometrika shows that for informational queries like 'how to choose [product],' a competitor's blog consistently outranks us in citations. We analyzed their article - it's twice as long, includes a video, and has a detailed comparison table. Hypothesis: If we completely overhaul our article, add a video review and an infographic, and make it the most comprehensive on the market, we can capture a share of those citations."
- Hypothesis 2 (PR): "Our GEO Score for branded queries ('[our brand] reviews') is low, and our monitoring tools show many neutral mentions without specifics. Hypothesis: If we provide 5 expert comments to major media outlets via HARO and distribute a research study through EIN Presswire, we will increase our brand's authority and improve its perception by AI."
- Result: You have a concrete, prioritized backlog of tasks for the content, PR, and technical teams for the next sprint, not just a vague goal to "improve the site."
Stage 3: Action - Executing the Plan with the Stack
- Tools: Your entire working stack from Blocks 2, 3, 4, and 5.
- Action: This is the stage of systematic work. The content team, using AI models and editing services, creates new material. The PR manager works with HARO and Brandpush. Technical specialists implement schema markup and fix errors. The SERM specialist addresses negative feedback found through Brand24.
- Result: Hypotheses are turned into tangible changes on your website and in the information field surrounding it.
Stage 4: Control - Re-measuring and Evaluating Effectiveness
- Tool: Geometrika.
- Action: After a set period (e.g., one month after implementing changes), you conduct a follow-up audit in Geometrika using the same query groups. You compare the new metrics with the baseline you established in the first stage.
- Result: You get a data-driven answer.
- Success Scenario: "Our GEO Score for the 'how to choose [product]' cluster grew from 15 to 50. Our new article is now cited in 60% of AI answers. The hypothesis was confirmed; the strategy is working."
- Failure Scenario: "The GEO Score hasn't changed. The AI still prefers the competitor. Our hypothesis was incorrect or insufficient. We need to conduct a deeper analysis of the competitor's content and form a new hypothesis for the next cycle."
After this fourth stage, the cycle begins again. You re-analyze the data, set new tasks, and execute them.
It is this data-driven, cyclical approach of "Measure - Plan - Act - Control" that distinguishes professional Generative Engine Optimization from random attempts to "please the AI." It turns GEO into a manageable engineering process with predictable, albeit not always successful, iterations. And at the very center of this approach, in the measurement and control stages, there must always be a precise, objective, and specialized measurement tool. Without it, the entire system is blind.